BOC Sciences is proud to provide you enzyme conjugation and modification services to be used as signal generating molecules. Our experts and chemists are professional at enzyme labeling to help you to make progress in your research. Moreover, our dedicated technical account managers will guide your project through every step of the process and constantly keep you informed of the latest project progress.
Enzyme labeling is a method used in bioanalysis in which chemical markers are placed on molecules within a substance. Molecular tags allow the detection and tracking of molecules in substances during chemical analysis or testing. Different types of tags can be used for this type of biolabel. When one enzyme is chemically bound to another molecule, this process is called enzyme labeling. Enzymes such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (ALP) can bind to antibodies, oligonucleotides, peptides or proteins, thus acting as signal molecules in a variety of applications.
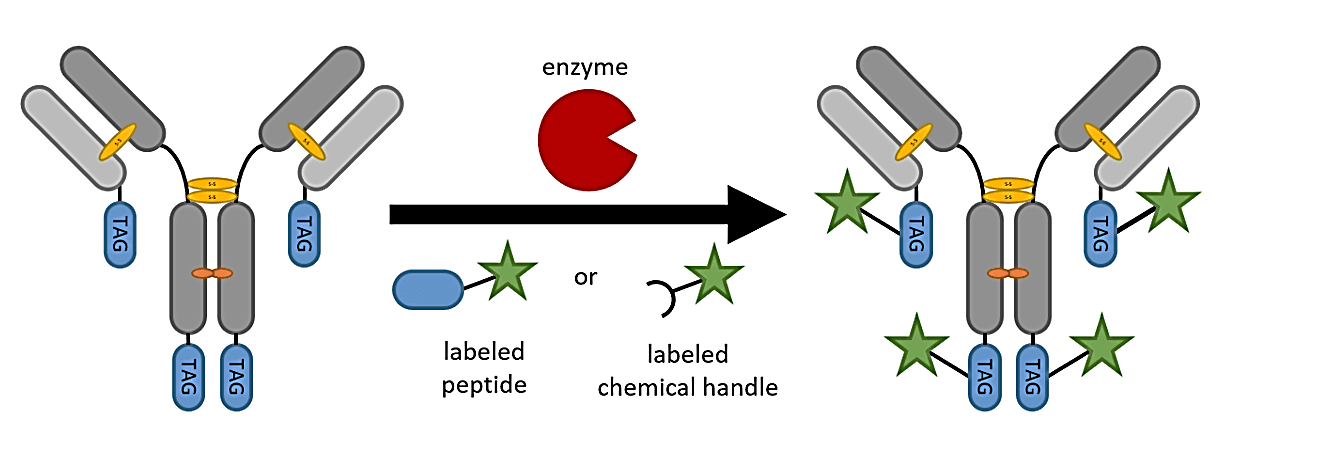
Enzyme-labeled molecules are biomolecules that have been conjugated with enzymes to serve as detectable markers in assays. These enzyme labels enhance sensitivity by generating measurable signals during reactions, making them essential in immunoassays, nucleic acid detection, and protein analysis. Common enzyme labels include HRP and ALP, which provide strong signal amplification and reliability across biochemical applications. Understanding how enzyme-labeled systems function is critical for selecting the right assay format and improving data accuracy.
Tagging enzymes involves attaching detectable chemical groups or enzymes to biomolecules for tracking and analysis. Several strategies are commonly applied:
Covalent bonding: creating stable chemical links between enzymes and biomolecules to ensure long-term activity in assays.
Biotin–streptavidin systems: using high-affinity biotin binding to achieve flexible and reversible tagging for multiple experimental designs.
Linker chemistry: employing specialized linkers to control spacing and orientation, preserving the biological activity of both enzyme and target.
These tagging strategies support a wide range of applications: monitoring biochemical pathways, confirming molecular interactions, validating assay results, and enabling detection in diagnostics, therapeutic monitoring, and environmental testing. By choosing the appropriate tagging method, researchers can expand experimental scope and improve data accuracy.
In addition to standard labeling methods, BOC Sciences provides custom enzyme labeling and development services tailored to unique project requirements. Whether clients need specialized conjugation chemistries, novel enzyme formulations, or scale-up support, our scientific team designs optimized strategies for each case. Customized services are particularly valuable for emerging research areas such as biosensor development, new diagnostic platforms, and advanced therapeutic assays. This flexibility ensures that clients can achieve precise, efficient, and cost-effective labeling outcomes beyond conventional solutions.
The enzyme labeling process usually follows a systematic workflow:
Following this step-by-step process provides researchers with reliable, reproducible results that can be adapted to different research and industrial applications.
We provide enzyme labeling services that maintain biological activity while improving detection sensitivity. Our methods support multiple assay formats, delivering reliable and reproducible results across applications.
Submit your inquiry to request a custom solution.
References
If you have any questions or encounter issues on this page, please don't hesitate to reach out. Our support team is ready to assist you.