BOC Sciences' R&D team has years of experience in chiral synthesis and can provide comprehensive synthesis services. We focused on customized synthetic services, which can efficiently carry out pilot scale-up, technical verification and commercial production, ensuring product quality stability and safety and saving time and cost for customers.
Chiral synthesis is a type of chemical synthesis that involves the creation of chiral molecules, which are molecules that are not superimposable on their mirror image. In other words, chiral molecules have a "handedness," like a left hand and a right hand, and cannot be superimposed on their mirror images, like a left hand cannot be superimposed on a right hand.

The importance of chirality lies in its profound impact on biological systems. In pharmaceuticals, one enantiomer of a drug may deliver the intended therapeutic effect, while the other could be less active or even cause undesired outcomes. This makes the control of chirality a decisive factor in modern drug design and synthesis.
Optical activity, a measurable property of chiral compounds, reflects their ability to rotate plane-polarized light and serves as a direct indicator of enantiomeric composition. Understanding and controlling optical activity not only helps ensure the safety and efficacy of active pharmaceutical ingredients but also provides valuable insights into molecular interactions, stereoselective synthesis, and quality consistency across production scales.
Enantiomeric purity: Many biologically active compounds have chiral centers and only one enantiomer may be effective while the other may be inactive or even harmful. Chiral synthesis allows for the production of single enantiomers with high enantiomeric purity, which is essential for the safety and efficacy of the drug.
Improved pharmacokinetics: Stereochemistry can influence the pharmacokinetics of drugs. For example, the enantiomers of a drug may have different rates of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Enantiomerically pure drugs that have improved pharmacokinetic properties and reduced side effects can be produced by chiral synthes.
Biocatalysis: Biocatalysis is the use of biological compounds (enzymes or live cells) to perform and speed up chemical transformations. Advantages of biocatalysts are commonly recognized by the industry. Yeast is a typical biocatalyst for the chiral reduction of ketones.
Chiral pool synthesis: Chiral pool synthesis is one of the simplest approaches for chiral synthesis. The desired target molecule is obtained by successive reactions of chiral starting materials with achiral reagents. So, chiral pool synthesis is necessary if a new chiral species will be created in SN2 reaction.
Enantioselective catalysis: Generally, enantioselective catalysis involves chiral coordination complexes. The catalysts are rendered chiral by using chiral ligands. A typical example of enantioselective catalysis is asymmetric hydrogenation, which could reduce a wide range of functional groups.
Organocatalysis: Organocatalysis is a catalysis that increases the rate of chemical reactions, but the organic catalysts only consist of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other non-metal elements. If the organocatalyst is chiral, enantioselective synthesis can be achieved.
Enzymatic synthesis: Using enzymes to catalyze the formation of chiral molecules. Enzymes have highly selective and can create chiral molecules with high enantiomeric excess.
Resolution: using methods such as chromatography or crystallization to separate a racemic mixture (a mixture of both enantiomers) into its individual enantiomers.
The chiral auxiliary is a compound or unit temporarily added to organic synthesis to control the synthesis of stereochemistry. By adding the chiral auxiliary, the prochiral substrate can be transformed into a chiral product. Moreover, the auxiliary can typically be recycled for future use.
Building block is a term in chemistry used to describe a virtual molecular fragment or a real chemical compound whose molecules possess reactive functional groups. As for chiral building blocks, they are valuable intermediates in the synthesis of natural products and pharmaceuticals.
Chiral catalysts can be applied in asymmetric synthesis such as alkylation, Diels-Alder reaction, asym-metric reduction, hydroformylation, epoxylation, and dihydroxylation. The relationship between the chiral catalyst and the reaction system is just like the relationship between a lock and a key, which is highly selective.
The design of chiral ligands is frequently based on C2-symmetry to reduce the number of diastereomeric intermediates and transition states that play a role in the catalytic cycle.
The chiral resolution, as an important tool in the production of optically active drugs, is a process for the separation of racemic compounds into their enantiomers in the aspect of stereochemistry.
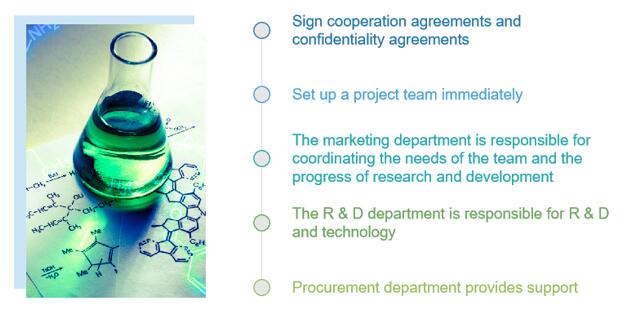
At BOC Sciences, we provide various types of synthesis methods including biocatalysis, chiral pool synthesis, enantioselective catalysis, chiral auxiliaries catalysis, and organocatalysis. We also use multiple techniques (NMR, LCMS, GCMS, X-ray) to analyze compounds after completing the chiral synthesis. Our experts will work with you to optimize the synthetic routes and approaches. According to your needs and the properties of chemical substances, a wide range of custom services are available in our laboratory.
We provide chiral synthesis with high enantiomeric purity, stereochemical control, and scalability to support complex chemical projects.
Submit your inquiry to request a custom solution.
If you have any questions or encounter issues on this page, please don't hesitate to reach out. Our support team is ready to assist you.